Today we will take our first detailed look at the Sessions screen. The sessions screen lets you view applications connected to the database and see what they’re doing and how many resources they are consuming.
You launch the Sessions screen by pressing the ‘l’ (lowercase ‘L’) key. When db2top is at its minimum width of 80 columns, the Sessions screen consists of a set of gauges at the top and a table at the bottom.
The gauges, as they appear in db2top, are shown below:
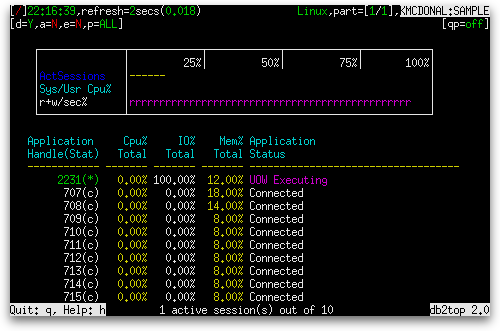
There are three gauges shown:
| Gauge Name | Gauge Type | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| ActSessions | Normal | Proportion of connections that are executing work. (rem_cons_in_exec + local_cons_in_exec) / (rem_cons_in + local_cons) |
| Sys/Usr Cpu% | Avg Seconds |
where:
|
| r+w/sec% | Avg Seconds |
where:
|
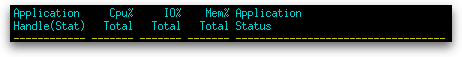
The table below the gauges has the following columns, grouped into sets large enough to fit a small screen:
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Application Handle(Stat) | A system-wide unique ID for the application (agent_id), together with a short code for the current status of the application (appl_status) in parentheses. Possible values for the status are:
|
| Cpu% Total |
This session’s statement CPU time as a percentage of the total statement CPU time of all sessions (stmt_usr_cpu_time + stmt_sys_cpu_time) / sum(stmt_usr_cpu_time + stmt_sys_cpu_time) * 100%, where sum() means summed across all sessions. A sliding window is used to measure only the last x samples, where x is a number between 1 and 30 that the user can control using the ‘+’ and ‘-‘ keys. |
| IO% Total |
( |
| Mem% Total |
The current size of this session’s memory pool as a percentage of the size of all sessions’ memory pools combined. pool_cur_size × 100% / sum( pool_cur_size ) where sum() means summing across all sessions |
| Application Status | The current status of the application (appl_status). Possible values are:
If a rollback is in progress, its progress ( If the status short code from the Application Handle column is ‘*’, the color is magenta. If the status short code from the Application Handle column is ‘l’, the color is red. |
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
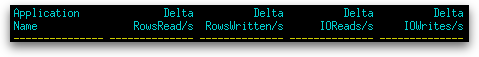
| Application Name | The name of the application (appl_name) running at the client, as known to the database or DB2® Connect™ server. |
|
|
|
|
|
pool_data_l_reads + |
|
|
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
|
|
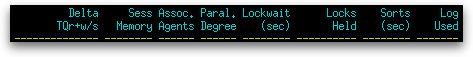
| Sess Memory | The current size of the session’s memory pool (pool_cur_size). |
| Assoc. Agents | The number of subagents associated with the application (num_assoc_agents). |
| Paral. Degree | The degree of parallelism requested when the query was bound (degree_parallelism). |
| Lockwait (sec) | The total elapsed time in seconds spent waiting for locks. lock_wait_time / 1000 |
| Locks Held | The number of locks currently held (locks_held) |
| Sorts (sec) | The total elapsed time in seconds for all sorts that have been executed. total_sort_time / 1000 |
| Log Used | The amount of log space (in bytes) used in the current unit of work of the monitored application (uow_log_space_used). |
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
|
|
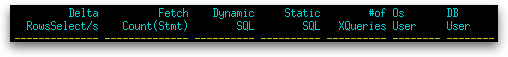
| Fetch Count(Stmt) |
|
| Dynamic SQL | The number of dynamic SQL statements that were attempted (dynamic_sql_stmts). |
| Static SQL | The number of static SQL statements that were attempted (static_sql_stmts). |
| #of XQueries | The number of XQuery statements executed for an application or database (xquery_stmts) |
| Os User | The ID that the user specified when logging in to the operating system. This ID is distinct from auth_id, which the user specifies when connecting to the database (execution_id). When the execution_id is not available, the name of the database manager instance is shown instead (server_instance_name). |
| DB User | The authorization ID of the user who invoked the application that is being monitored (auth_id). When the auth_id is not available, the name of the database manager instance is shown instead (server_instance_name). |
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
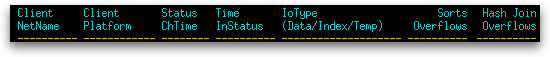
| Client NetName | The nname in the database manager configuration file at the client database partition. This element only applies to Windows Environments where the NetBIOS LAN environment exists. |
| Client Platform | The operating system on which the client application is running (client_platform). |
| StatusChTime | The date and time the application entered its current status (status_change_time). |
| Time InStatus | The amount of time spent so far in the current state (time of most recent snapshot – status_change_time). |
| IoType (Data/Index/Temp) | An in-table gauge showing the proportion of total reads that are logical data reads, logical index reads, and logical temporary reads. Data reads (pool_data_l_reads) are shown by a sequence of ‘d’ characters, index reads (pool_index_l_reads) by a sequence of ‘i’ characters, and temporary reads (pool_temp_data_l_reads + pool_temp_index_l_reads) by a sequence of ‘t’ characters.
|
| Sorts Overflows | The total number of sorts that ran out of sort heap and may have required disk space for temporary storage (sort_overflows). |
| Hash Join Overflows | The number of times that hash join data exceeded the available sort heap space (hash_join_overflows) |
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Client Pid | The process ID of the client application that made the connection to the database (client_pid). |
| Node Number | The number assigned to the node in the db2nodes.cfg file (node_number). |
| Last Operation | The statement operation currently being processed or most recently processed, if none currently running (stmt_type) |
| TimeTo Connect | The time it took for this session’s connection to be established (conn_complete_time – appl_con_time). |
| Session Cpu | The total system and user CPU time used by the database manager agent process (usr_cpu_time + sys_cpu_time). |
| Statement Cpu | The total user and system CPU time used by the currently executing statement (stmt_usr_cpu_time + stmt_sys_cpu_time). |
| Max Cost Estimate | The most recent estimated cost of a query in the current transaction of the session, as determined by the SQL compiler (query_cost_estimate). |
| Recent Cpu[1 to 30] | This session’s statement CPU time (stmt_usr_cpu_time + stmt_sys_cpu_time). A sliding window is used to measure only the last x samples, where x is a number between 1 and 30 that the user can control using the ‘+’ and ‘-‘ keys. |
So that covers what information is available on small screens of 80 to 140 columns wide. In the next post, we’ll see what additional information becomes available on wider screens.



Pingback: db2top Sort « The K Guy()